Stanford University researchers have developed a breakthrough solar panel that generates electricity at night, reducing reliance on batteries. This innovative technology utilizes radiative cooling to harness the heat dissipating from surfaces at night, providing a new solution for off-grid solar systems.

Converting Night Skies into Electricity Power Supplies
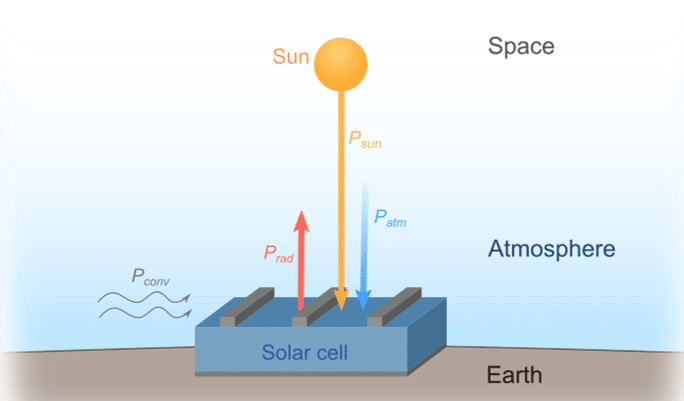
Radiative cooling is experienced when a surface cools more, so on clear nights, it emits infrared radiation into space. This heat falls because of the currently weak thermoelectric materials utilized in the solar panels. However, researchers can harness this heat to generate electricity by placing thermoelectric generators on the solar panels. The amount of power obtained (approximately 50 mW/m2) is relatively small relative to what is produced during the day. But it is enough for the functioning of low-powered devices such as LED lamps and sensors, respectively, in off-grid areas.
Meeting Nighttime Energy Demands

Unlike their counterparts that rely solely on sunlight for power. These home solar panels function and provide crucial power in areas where solar energy is rare. That is why, considering that at least 770 million people have no access to electricity all around the globe,-modules for nighttime can contribute to lighting and power supply in the regions with no central electricity. Besides, it can be integrated into existing solar systems, so no expensive batteries are needed, making renewable energy more affordable and more reliable.
Reducing Battery Dependence

Nighttime solar panels reduce the dependence on costly batteries and an additional strain on the environment. These panels produce electricity for small consumers including IoT networks and environmental monitoring systems; doing so minimizes the effects that come with battery production and recycling.
Expanding Applications of Radiative Cooling
Beyond solar energy, radiative cooling technology has other exciting applications, such as:
- SkyCool Systems provides a zero-energy air conditioning solution.
- ETH Zurich has adopted the principle of creating potable water in drought-prone areas
These innovations highlight the broad potential of radiative cooling in advancing sustainability across various industries.

Bridging the Energy Gap

Nighttime solar panels guarantee a round-the-clock energy supply irrespective of day or night. This capability strengthens the reliability of solar energy in areas with fluctuating or low weather conditions and thus encourages the use of solar energy systems at the global level. Whether solar for homes or commercial giant PV systems, these panels connect the demand and supply issues and provide clean energy to remote places.
Conclusion
Nighttime solar panels are one of the biggest breakthroughs in solar power solutions. Some new opportunities with these panels by drawing upon the radiative cooling technology that uses the night sky as the heat sink. Over time, with the continued research and development of the systems, the cost of laying down the solar panels is likely to come down, which will in turn offer improved services in using solar energy. It can massively transform how solar systems are deployed across households and other establishments bringing in a cleaner energy future.
